Absolutely! Here’s a 3000-word article about power plants, structured with `
` and `
` tags in place of “ for a more organized and readable format.
Power plants are the backbone of modern civilization. They are the facilities that convert various forms of energy into electricity, which powers our homes, industries, and transportation systems. Understanding how these complex systems work is crucial for appreciating the infrastructure that sustains our daily lives.
Electricity is an indispensable part of our lives. From the moment we wake up and turn on the lights to the continuous operation of our digital devices, we rely on a constant supply of power. Power plants are the engineering marvels that make this possible. They are the intricate systems that harness energy from natural resources and transform it into usable electricity.
At the heart of every power plant is the principle of energy conversion. Energy exists in various forms, such as chemical, thermal, kinetic, and nuclear. Power plants take one of these forms of energy and convert it into electrical energy. This conversion typically involves several stages, each with its own set of technologies and processes.

Power plants can be categorized based on the primary energy source they use. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, impacting its efficiency, environmental impact, and cost.
Thermal Power Plants
Thermal power plants generate electricity by heating water to produce steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator. These plants are the most common type globally, utilizing various fuels.
Coal-Fired Power Plants

Coal-fired power plants burn coal to heat water. The combustion process releases heat, which is used to boil water and create high-pressure steam. This steam then spins a turbine, which in turn drives an electrical generator.
Process: Coal is pulverized and burned in a boiler. The heat from combustion turns water into steam. The steam spins a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity.
Natural Gas Power Plants
Natural gas power plants burn natural gas to heat water or directly drive a gas turbine. Combined-cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plants are highly efficient, using both gas and steam turbines.
Process: Natural gas is burned in a combustion chamber, producing hot gases that drive a gas turbine. The waste heat from the gas turbine is used to generate steam, which drives a steam turbine.
Oil-Fired Power Plants
Oil-fired power plants burn fuel oil to generate steam. These plants are less common due to the high cost of oil and environmental concerns.
Process: Fuel oil is burned in a boiler to produce steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator.
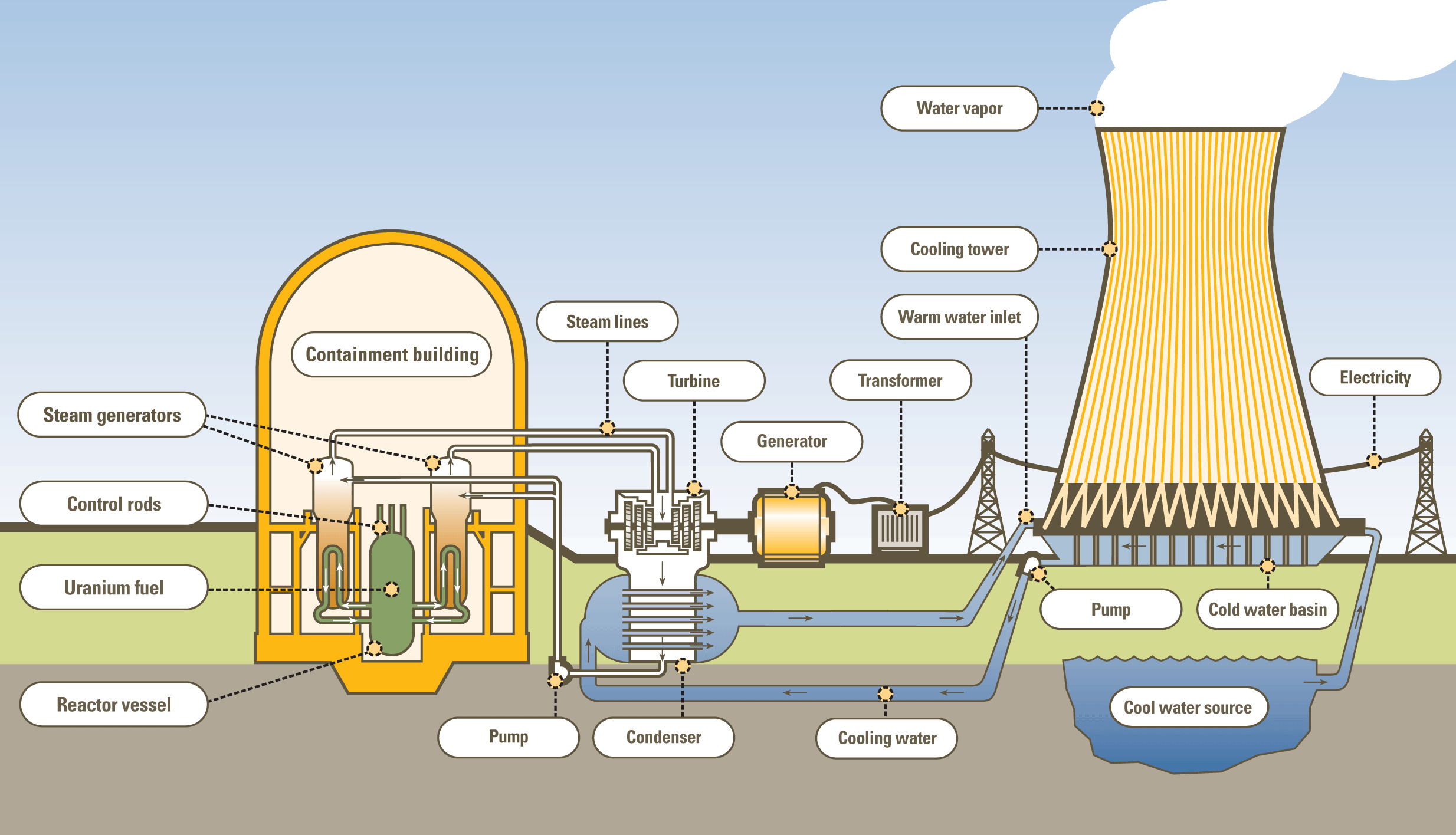
Nuclear Power Plants
Nuclear power plants use the heat generated from nuclear fission to produce steam. They offer a low-carbon alternative but raise concerns about nuclear waste and safety.
Process: Nuclear fission in a reactor core generates heat. This heat is used to produce steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator.
Renewable Energy Power Plants
Renewable energy sources are gaining prominence due to their lower environmental impact and sustainability.
Hydroelectric Power Plants
Hydroelectric power plants use the kinetic energy of flowing water to drive turbines.
Process: Water stored in a reservoir flows through a turbine, which drives a generator.
Solar Power Plants
Solar power plants convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells or concentrated solar power (CSP) systems.
Photovoltaic (PV) Plants:
Wind Power Plants
Wind power plants use wind turbines to convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity.
Process: Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy, which drives a generator.
Geothermal Power Plants
Geothermal power plants use heat from the Earth’s core to produce steam and generate electricity.
Process: Geothermal energy heats water or steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator.
The Future of Power Plants
The future of power plants is trending towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. Advances in renewable energy technologies, energy storage, and grid modernization are paving the way for a transition to a low-carbon energy system.
Power plants are essential infrastructure that supports modern society. Understanding their various types, processes, and impacts is crucial for making informed decisions about our energy future. As we move towards a more sustainable and low-carbon future, the evolution of power plant technologies will play a critical role.



