Absolutely! Here’s a comprehensive 3000-word article on USDA plant Hardiness Zones, structured with `
` and `
` headings.
Gardening success hinges on understanding your local climate. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is an indispensable tool for gardeners across the United States, providing a clear picture of average minimum winter temperatures. This guide will delve into the intricacies of these zones, their importance, and how to use them effectively.
What Are USDA Plant Hardiness Zones?
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides the United States into 13 zones, each representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference in the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature. These zones help gardeners determine which perennial plants are most likely to survive the winter in their location.
The Significance of Minimum Winter Temperatures
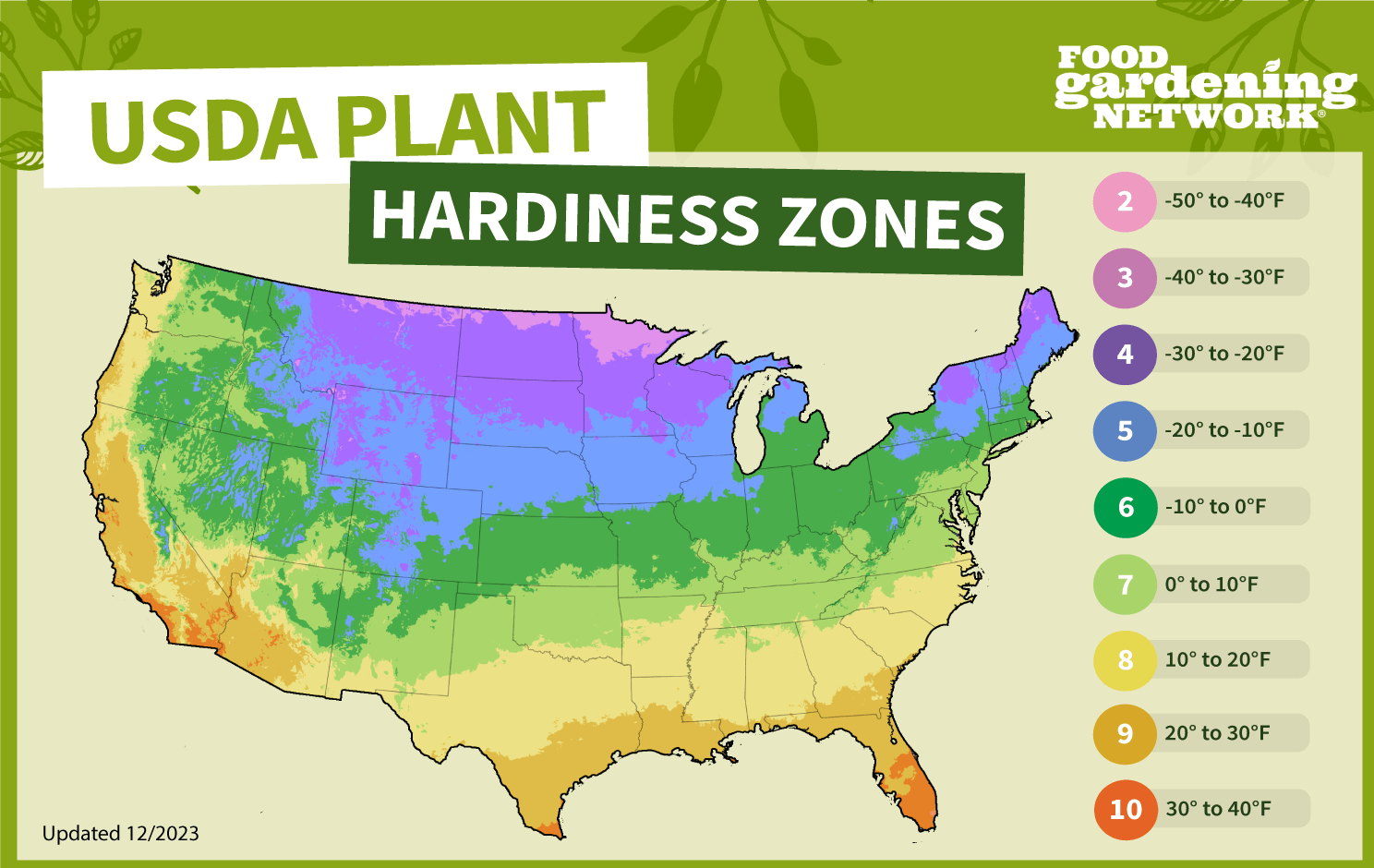
Plant survival: Perennial plants must withstand the coldest temperatures of the year to survive and thrive.
Understanding the Zone Numbers
Zone 1: Represents the coldest regions, with very low minimum temperatures.
The History and Evolution of the USDA Map
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map has evolved over time, reflecting advances in data collection and changes in climate.
Early Developments
Initial maps: Early versions of the map were less detailed and based on limited data.
Recent Updates
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ms-usda-gardening-zone-3a925f9738ce4122b56cde38d3839919.jpg)
2012 update: The 2012 update incorporated more recent temperature data and improved mapping technology.
How to Use the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Using the map effectively requires understanding how to locate your zone and interpret the information.
Finding Your Zone
USDA website: The USDA website provides an interactive map and a zip code search tool.
Interpreting Zone Information
Plant tags: Plant tags often indicate the recommended hardiness zones.
Microclimates
Urban heat islands: Cities tend to be warmer than surrounding rural areas.
Factors Beyond Hardiness Zones
While hardiness zones are crucial, other factors influence plant survival.
Soil Conditions
Soil type: Different plants prefer different soil types (e.g., sandy, clay, loam).
Sunlight Exposure
Full sun: Requires at least six hours of direct sunlight per day.
Moisture Levels
Water requirements: Different plants have varying water needs.
Plant Selection and Zone Considerations
Choosing the right plants for your zone is essential for a thriving garden.
Perennial Plant Selection
Zone-appropriate plants: Select perennials that are rated for your hardiness zone.
Annual Plant Selection
Frost dates: Consider your area’s average last and first frost dates.
Native Plants
Adaptation: Native plants are well-adapted to local conditions.
The Impact of Climate Change on Hardiness Zones
Climate change is causing shifts in temperature patterns, affecting hardiness zones.
Shifting Zones
Warmer temperatures: Average minimum winter temperatures are increasing.
Adapting to Change
Monitoring updates: Stay informed about updates to the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
Additional Gardening Resources
Numerous resources can help you further understand and utilize hardiness zones.
USDA Resources
USDA website: The official USDA website provides detailed information and interactive tools.
Gardening Organizations
Local garden clubs: Connect with local gardeners for advice and support.
Online Gardening Resources
Gardening websites: Many websites offer zone-specific planting guides and advice.
By understanding and utilizing the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, gardeners can make informed decisions, ensuring a healthy and thriving garden.



